Traceable’s API Security Testing (AST) allows you to integrate an authentication mechanism into your scans. This is particularly useful when authentication tokens are short-lived or have expired, as expired credentials can prevent scans from completing successfully. For instance, a scan run on live traffic after a long interval may fail if the authentication has expired. DAST scans that rely on OpenAPI specifications can be affected in the same way. Scans on older or suppressed data may also encounter issues if the associated authentication tokens are no longer valid. In these situations, AST requires a fresh authentication token to complete the scan.
Note
The topic assumes that you have reasonable knowledge of authentication mechanisms. For the list of available authentication mechanisms, see Supported authentication mechanisms.
What will you learn in this topic?
By the end of this topic, you will be able to understand:
The various authentication mechanisms available in AST.
The roles available for the above authentication mechanisms.
The steps to navigate the Authentication page and set up authentication.
Supported authentication mechanisms
Traceable supports multiple authentication mechanisms, such as:
Authentication Mechanism | Description |
|---|---|
API Key | Authenticates requests using a static key sent in a header, query parameter, or cookie. For more information, see API Key. |
Basic Auth | Authenticates by sending a Base64-encoded username and password in the request header. For more information, see Basic Auth. |
Bearer | Authenticates requests and grants access using a token that the server trusts based solely on possession. For more information, see Bearer. |
Content Signature | Authenticates by signing the request body with a private key, allowing the server to verify integrity. For more information, see Content Signature. |
HMAC | Verifies request integrity and authenticity using a cryptographic hash generated with a shared secret. For more information, see HMAC. |
JWT | Uses a signed, self-contained token carrying user claims for authentication and authorization. For more information, see JWT. |
Mutual TLS | Authenticates both client and server using TLS certificates during the handshake. For more information, see Mutual TLS. |
OAuth | Delegates access using authorization flows where the server issues tokens instead of sharing credentials. For more information, see OAuth. |
PoP Token Signature | Authenticates by requiring the client to sign each request with a key embedded in the token. For more information, see PoP Token Signature. |
Custom Auth | Allows defining a user-specific authentication mechanism using custom logic. For more information, see Custom Auth. |
Feature support matrix for authentication mechanisms
The following matrix outlines how each authentication type aligns with form support, code editability, and AI-generated configurations:
Auth Type | Form Type Support | Editable Code | AI-Generated Code |
|---|---|---|---|
API Key | ✔️ | ✔️ | ✔️ |
Basic Auth | ✔️ | ✔️ | ✔️ |
Bearer | ✔️ | ✔️ | ✔️ |
Content Signature | ✔️ | ✔️ | ✔️ |
HMAC | ✔️ | ✔️ | ✔️ |
JWT | ✔️ | ✔️ | ✔️ |
Mutual TLS | ✔️ | ✔️ | X |
OAuth | ✔️ | X | X |
PoP Token Signature | ✔️ | ✔️ | ✔️ |
Custom Auth | X | ✔️ | ✔️ |
Roles associated with authentication mechanisms
You can associate each authentication method with one of the following roles.
Standard
Admin
Reader
Writer
Roles define user capabilities, such as view-only or admin actions, allowing the authentication hook to dynamically apply the correct authorization logic and enhance coverage for access-control scenarios.
Navigating the page
To configure an authentication, navigate to Testing → Authentication, and click Configure Authentication in the page’s top right corner.
Configuring an authentication mechanism
In the Configure Authentication slide-out window, do the following:
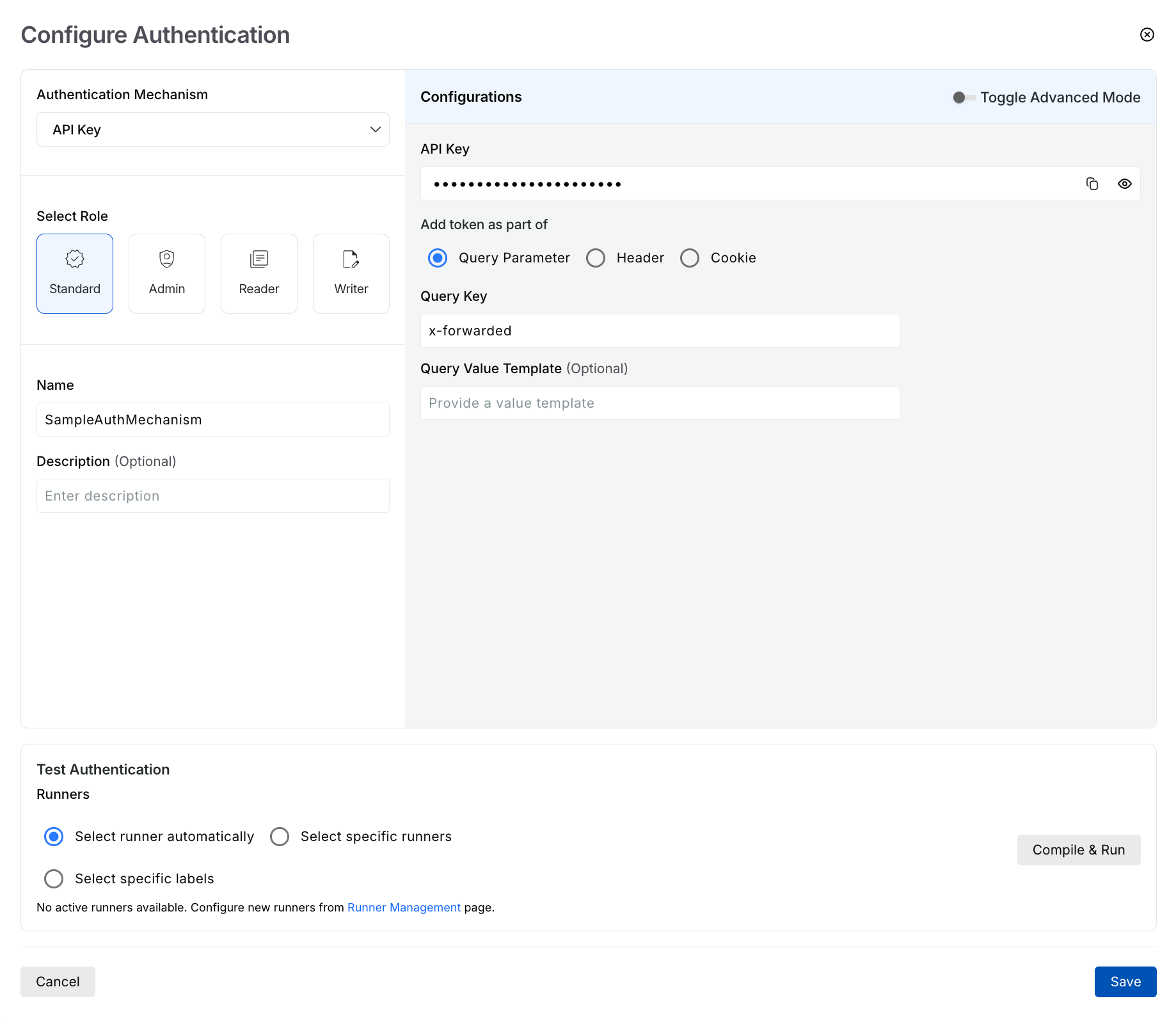
Authentication Configuration
Select the Authentication Mechanism from the drop-down list.
Select the Role you wish to assign.
Specify a Name for the authentication. This is the name you use to identify the authentication mechanism when creating a scan.
(Optional) Specify a Description for the mechanism.
Do one of the following:
Specify the configurations according to your requirements.
Click the Advanced Mode toggle and write a custom script for the authentication mechanism.
For more information on the available configurations under a mechanism, see the respective documents.
Test the authentication mechanism (except for OAuth) to ensure it accurately complies with the specified configurations.
For frequently asked questions about authentication and how Traceable stores credentials, see FAQs.