Updates (October 2025 to December 2025)
November 2025 — Updated the topic to add information about the availability of an exclusion type in the TPA version 1.49.0 and above. For more information, see Creating an Exclusion.
Exclusions enable you to create rules that exclude specific requests from being monitored, blocked, or allowed based on defined criteria. You can apply these exclusions to certain environments, sources, or threat types, ensuring more precise control over detection and response. You can create multiple rules and manage them according to your security needs.
What will you learn in this topic?
By the end of this topic, you will be able to understand:
The supported exclusion types and how you can leverage them.
Steps to create Exclusions in Traceable.
The actions that you can take on exclusions.
Supported exclusion types
Traceable allows you to create exclusion rules based on your defined rules. These rules help you configure the following exclusion types:
Exclude from Monitoring — This option is useful when you do not wish to monitor requests that match your configured criteria. For example, excluding monitoring from all emails with the testing.com domain. As a result, the request is not visible in the Traceable platform.
Exclude from Blocking — This option is useful when you do not want to block specific data from requests that match your configured criteria. For example, you can exclude data from being blocked (allow) when it comes from Hosting Provider IP types.
Exclude from Allow — This option is useful when you do not want to allow specific data from requests that match your configured criteria. For example, data from the Afghanistan region can be excluded from being allowed (blocked).
Exclude from Threat Actor Scoring — This option prevents the threat actor score from being affected for specific requests that match your configured criteria. For example, when the same request is flagged by two rules, you can exclude one to prevent scoring it twice.
How are exclusions helpful?
Exclusions help you reduce unnecessary monitoring, blocking, and allowing, allowing you to focus on genuine threats. Using these exclusions, you can allow trusted traffic and enforce targeted blocking tailored according to your requirements. You can also minimize false positives and ensure that your security policies align with your organizational needs.
Creating an Exclusion
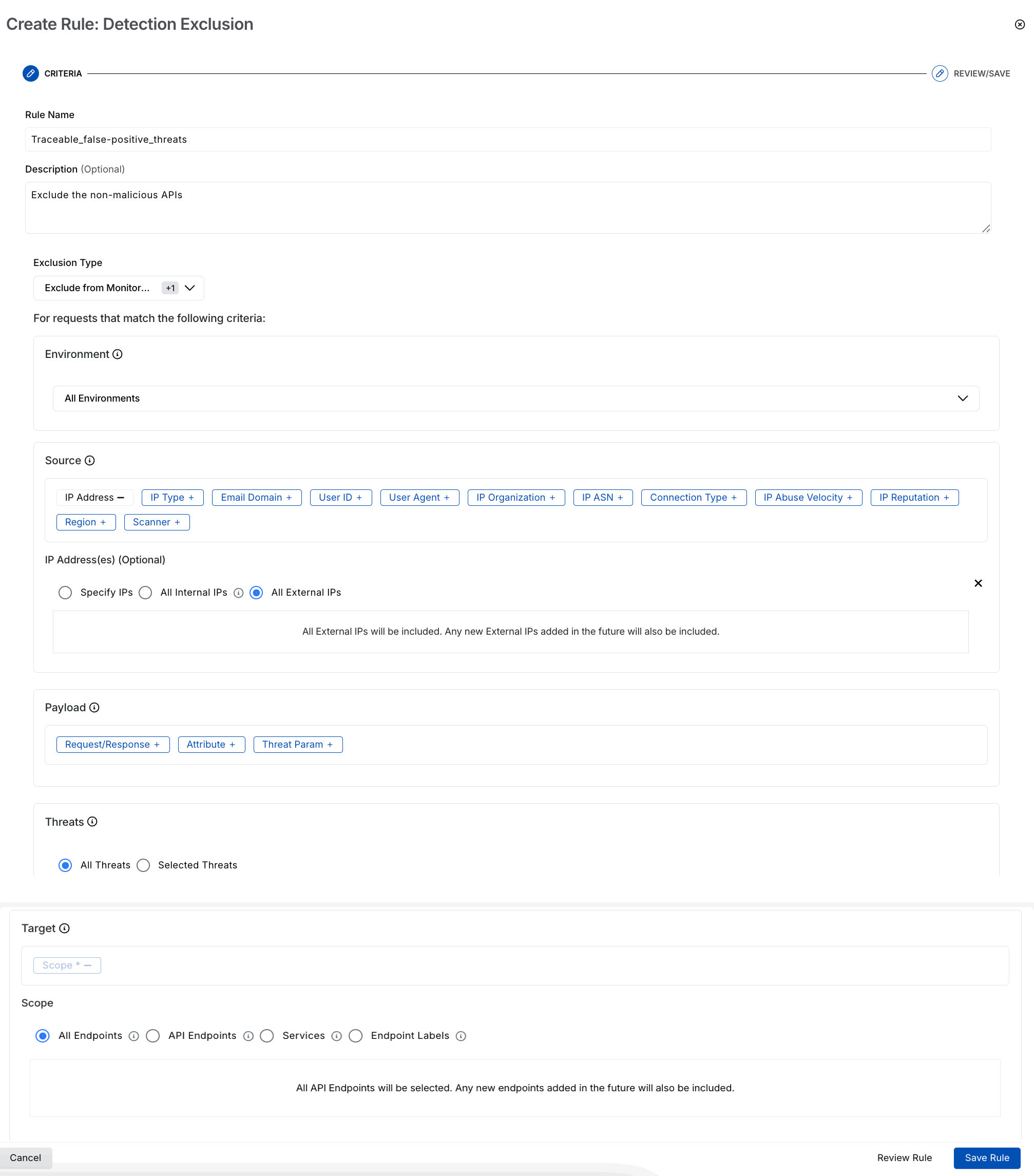
Navigate the Exclusions page under Protection → Settings, click + Add Rule, and complete the following steps to create an exclusion rule:
Exclusion Rule
Step 1 — Criteria
In the Criteria step of the Create Rule page, complete the following:
Specify the Rule Name, for example, Domain-level exclusion.
(Optional) Specify the rule Description.
From the Exclusion Type drop-down list, select the type of exclusion you want to configure, for example, Exclude from Monitoring.
Note
You can select one or more exclusion types according to your requirements. However, some attributes below may vary depending on your choice.
The Exclude from Blocking and Exclude from Allow options are only available for TPA version 1.49.0 and above.
From the Environment drop-down list, select the environment from which you wish to exclude events, for example, All Environments.
In the Source section, select the source from which you wish to exclude incoming data, such as an Email Domain ending with @traceable.ai.
Traceable supports the following sources for creating an exclusion rule:IP Address — Limit data from specific, internal, or external IPs.
IP Type — Control usage based on IP types, such as Anonymous VPN, Bot, Scanner, etc.
Email Domain — Limit requests from specific or a range of email domains, such as those belonging to a specific organization.
User ID — Manage traffic based on unique user IDs or regex for user IDs.
User Agent — Limit requests based on a user-agent regex that indicates the type of client, such as a bot or scripts making requests.
IP Organization — Manage traffic from specific entities known for spiking API request traffic.
IP ASN — Limit traffic from ASNs, which indicate the network provider from where the traffic originates.
Connection Type — Control data incoming from a specific connection type, such as Corporate or Data Center.
IP Abuse Velocity — Limit requests from IPs showing a high API abuse rate.
IP Reputation — Limit data coming from IPs with a poor reputation, such as those identified by threat intelligence.
Region — Enforce limits by geographic region, accounting for location-based traffic patterns.
Scanner — Manage traffic coming from automated testing tools, such as Traceable’s AST, etc.
Note
The availability of the above sources may vary depending on the Exclusion Type you select.
All Sources except IP Abuse Velocity and IP Reputation have an Exclude check-box corresponding to their value field. When you select that check box, Traceable applies the exclusion rule on all values except the ones you choose. For example, in the image above, Traceable excludes attacks or threats from all user IDs except the one selected.
In the Payload section, select the API component that Traceable should use to exclude events. For example, Attribute with the key as http.response.body.order.user.email and any value.
In the Threats section, select the threats you wish to exclude from the events. For example, Selected Threats with threat type as Authorization Bypass - User Level.
In the Target section, select the endpoint scope to which the exclusion should apply, such as All Endpoints.
Click Review Rule.
Step 2 — Review and Save
In the Review/Save step, review the attributes you configured in the Criteria step and click Submit. You can try out a hands-on demo to create an exclusion rule policy in Traceable, as shown below.
Demo and Example
The following interactive demo walks you through the steps to navigate and create exclusion rules under Protection.
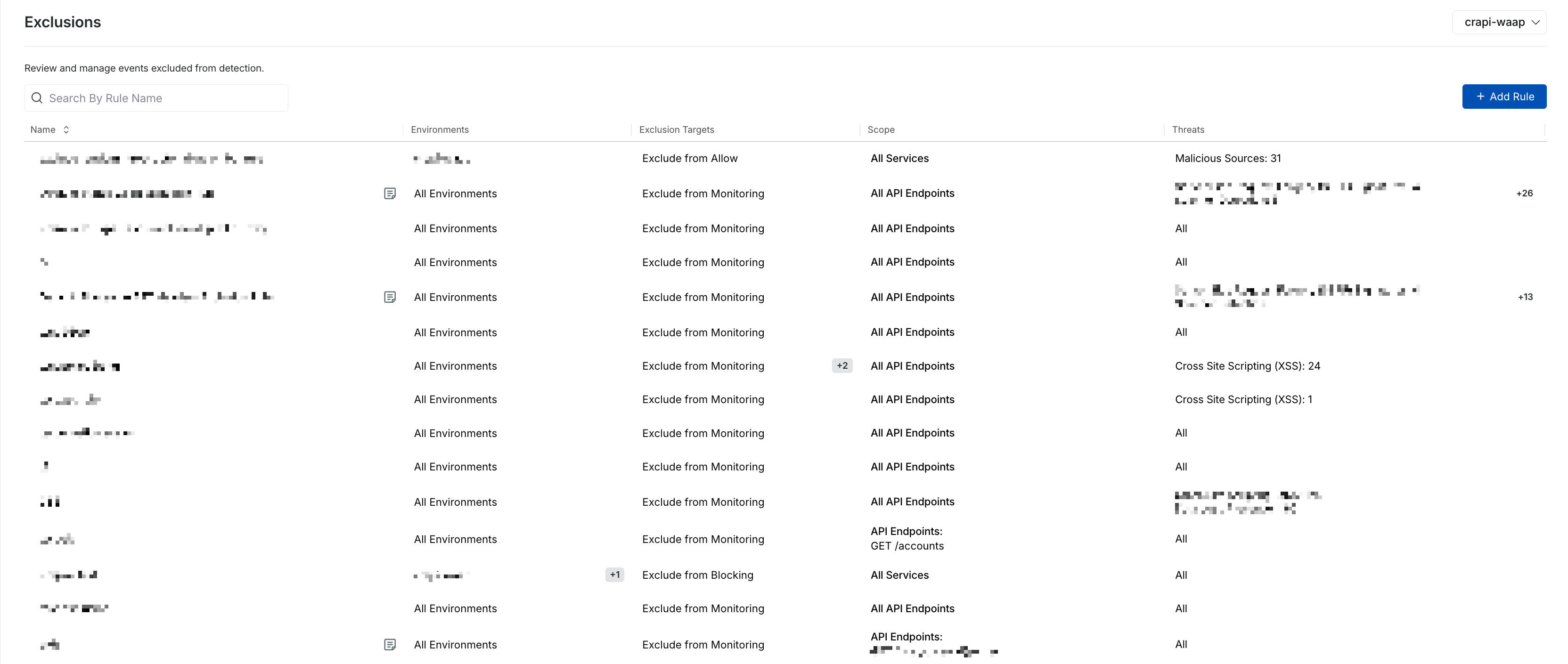
Exclusions View
The exclusion rule should be visible on the Exclusions page. You can perform the steps above to create multiple rules.
Exclusion Views
Actions on Exclusions
You can also perform the following actions on the policies by clicking on the Ellipse (![]() ) icon corresponding to a rule:
) icon corresponding to a rule:
Edit a rule to add or remove attributes according to your requirements.
View a rule to identify the attributes Traceable uses to exclude specific attacks or threat actors.
Clone a rule to create a copy of an existing rule with the same values as the existing rule.
Delete a rule.
Note
A deleted rule cannot be restored.